- Email: info@finobridge.com
- (+91) 96633 94131 | (+91) 98867 98339
With fuel prices soaring, commutingwhether short or long distancesis becoming increasingly costly. However, owning an electric vehicle allows you to travel comfortably without straining your budget. Additionally, electric vehicles are environmentally friendly; these zero-emission models do not emit harmful pollutants like their fuel-powered counterparts. They are also more cost-effective and simpler to maintain due to having fewer components compared to petrol and diesel vehicles. Furthermore, you can easily obtain a standard electric car insurance policy to cover both personal and third-party liabilities.

The battery pack is the energy storage system of an electric vehicle. It consists of multiple lithium-ion batteries that work together to power the motor and other essential systems. The capacity of the battery pack determines the driving range of the EV, with higher-capacity packs offering longer distances between charges.

The electric motor is the heart of an EV, replacing the internal combustion engine found in conventional cars. It converts electrical energy into mechanical power, propelling the vehicle forward. There are two main types of motors used in EVs: AC (Alternating Current) motors and DC (Direct Current) motors. Electric motors are known for their efficiency, quiet operation, and low maintenance requirements

The transmission system, often referred to as the gearbox, transfers power from the motor to the drive wheels, enabling the vehicle to move. Unlike internal combustion engine transmissions, EVs feature a direct transmission system rather than multi-speed gearboxes and lack a conventional transmission setup. Instead, electric vehicles are equipped with a straightforward drive mode selector.

The power control unit (PCU) is a crucial component in an electric vehicle. Its primary role is to convert the direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) during acceleration. The PCU comprises three key elements: the inverter, boost converter, and DC/DC converter. The inverter powers the motor and also assists in recharging the battery. The boost converter increases the voltage, while the DC/DC converter reduces the voltage as needed.
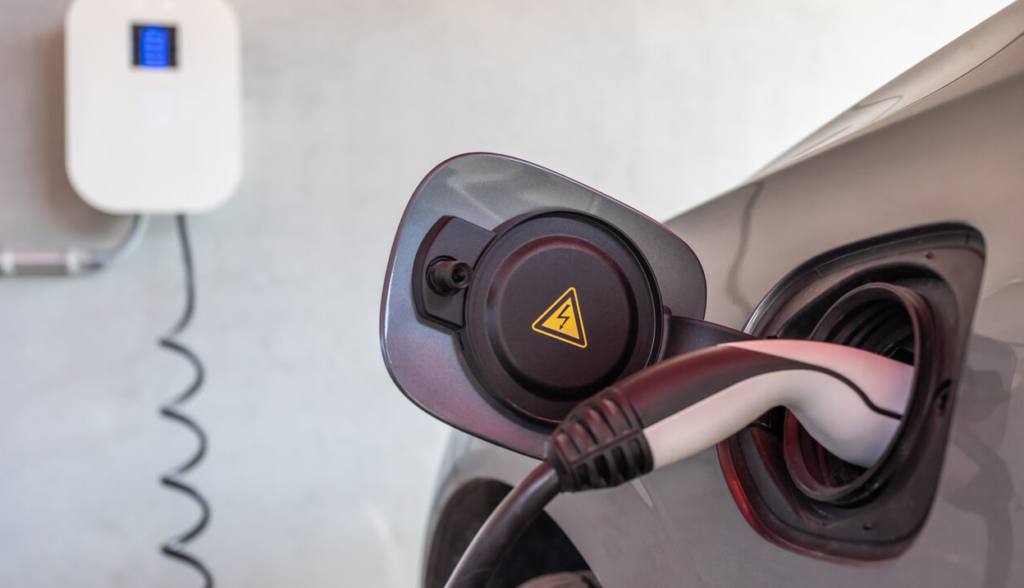

Charging System
The charging system includes the onboard charger, charge port, and various types of charging stations (home, public, and fast charging). While most EV charging happens at home, public and fast-charging stations are crucial for long-distance travel and for those without access to home charging.
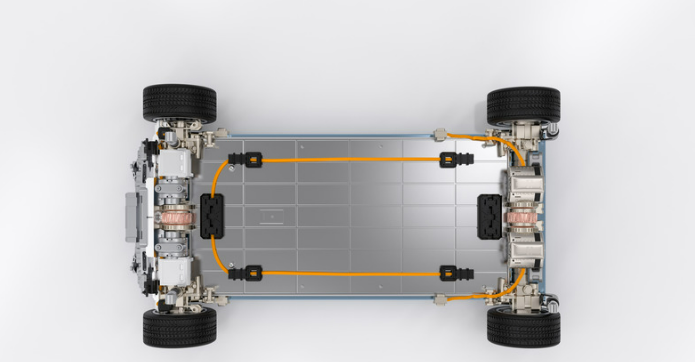
The BMS monitors and manages the health of the battery pack, ensuring safe and efficient operation. It balances the charge across individual cells, monitors temperature, and protects against overcharging and deep discharging.
We have tried to provide you the above information for illustrative purpose only. The range of an EV depends on its battery size; the higher the battery’s kWh, the more the mileage. Just like petrol and diesel cars, even electric cars vary in terms of size and price. What’s more, they are covered under car insurance, so you need not worry about this aspect either. A comprehensive car insurance policy will offer coverage against third-party liabilities, natural calamities, fire, and more, and save you from untimely expenses and losses.
Disclaimer: For more details, please refer to policy wordings and prospectus before concluding the sales.
Admin